Militarism Facts & Impacts on Women & Girls
Saturday, January 1, 2011
Militarism Facts & Impacts on Women & Girls
- Militarism is the combination of beliefs and practices that promotes a culture of fear and a continuum of violence. It is sustained through institutions, investments and structures based on the premise that the world is dangerous and armed force is the way to resolve conflicts.
- Militarism is a major obstacle to healthy democracies and the achievement of genuine human security. Since 9/11, the U.S. global “war on terror” has led to increased military budgets, the proliferation of weapons and arm sales, extra-judicial killings and torture, and security laws that permit governments to spy on civilians.
- In 2009, world military expenditure reached an estimated $1.5 trillion dollars, six percent higher than in 2008 and a 49 percent increase since 2000. Almost half (46.5%) of the world's military spending is done by the United States. The second highest is spent by China with 6.6 percent, France with 4.2% and the U.K. with 3.8 percent of the world's total.
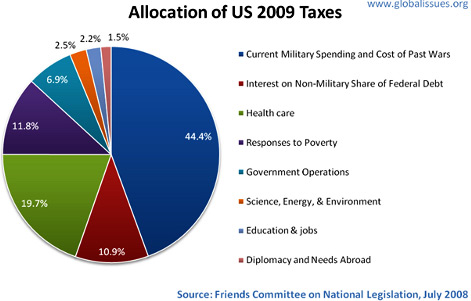
- If governments set aside ¼ of the $1.5 trillion in military spending, they could feed, clothe, educate and provide healthcare for the entire world's population. Although the UN was established to preserve peace through international cooperation and collective security, the UN's entire budget is only 1.8 percent of the world's military expenditures.
- In 2009, the U.S. spent $712 billion, or 44.4 percent, on defense. The lion's share isn't spent on protecting the American people but in fact on U.S. military activities throughout the world, including the estimated 1,000 U.S. military bases.
Facts about Militarism's Impact on Women
War and militarism disproportionately impact women and children. Whether forced to migrate due to conflict or targeted for sexual violence as a weapon of war, women and children bear the greatest costs. Here are some facts:
- Of the 50 million uprooted people around the world, women and children comprise 80 percent of the world's displaced persons by war and conflict.
- Civilians account for 80 percent of casualties of small arms.
- A 2001 study found that nations with greater gender equality were less likely to use violence in times of international crisis.
Rape as a Weapon of War
- In Rwanda, half a million women were raped during the 1994 genocide.
- In Bosnia and Herzegovina, up to 50,000 women of all ethnic groups were raped in what the International Criminal Court found was the systematic use of rape as a weapon of war.
- Up to 64,000 women were raped in Sierra Leone by armed combatants from 1991 to 2001. Half of internally displaced women who had direct contact with combatants were victims of sexual violence.
- Half a million women have been raped in the Democratic Republic of Congo in the past decade.
Impact on Women's Health
- In approximately 80 countries around the world, women are daily threatened by landmines, as women are the majority of those who gather food, water and firewood.
- According to our grantee partner Eco Center, in Eastern Kazakhstan where the Soviet Union tested the equivalent of 20,000 Hiroshima bombs, 1.5 million people have been exposed to nuclear poisoning and their entire food system contaminated. Cancer rates there are five times higher than the national average.
- In a study of the impact of chemical warfare on women, researchers found that Vietnamese women who were exposed, or whose husbands were exposed, to toxic herbicide dioxin ‘Agent Orange' experienced high rates of miscarriages and congenital birth defects. Two-thirds of their children had congenital defects or developed disabilities in their first year of life.
Impact on Children
- War is the primary factor in the creation of child refugees.
- In the past decade, conflicts and wars have killed two million children, wounded 6 million, and made 12 million children homeless.
- More than 300,000 boys and girls are “child soldiers.” Many of the girls are often forced into sexual slavery.
- In Nepal, when Maoists forces last February 2010 discharged 3,000 minors from their People's Liberation Army, 1,000 were girls.
